Thyroid & Parathyroid
What and where is the thyroid gland?
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland that consists of two halves connected by a bridge that sits in front of the windpipe. The thyroid gland is located in the lower part of the neck. It produces thyroid hormones which regulate your body’s metabolism.
There are a number of important structures close by to the thyroid gland. These are particularly relevant during thyroid surgery. The nerves that come to the voice box (the recurrent laryngeal nerves and the superior laryngeal nerves) as well as the parathyroid glands are both in close proximity to the thyroid gland. Injury to the nerves to the voice box is rare however it can cause a change (huskiness) in the voice. The function of these nerves is best done by an ENT surgeon using a fibreoptic telescope through the nose to visualize the vocal cords.
There are four parathyroid glands (two on each side) and these lie in close proximity to the thyroid gland. They are responsible for regulating calcium levels in the body. They may become overactive (either one gland or multiple) and need removal if the calcium levels are elevated. During thyroid surgery they may be at risk of injury. In this case, they are underactive and up to 20% of patients having the whole thyroid gland removed will need to take calcium replacement in the short term. This number is much less (2-3%) who require long-term thyroid replacement.
What are thyroid nodules?
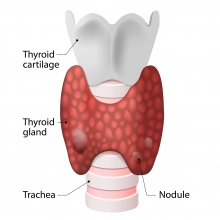
A thyroid nodule is a lump within the thyroid gland that is different to the surrounding gland structure. These are very common. It is estimated that up to 60-70% of people have thyroid nodules. Thankfully very few of these are cancers (less than 5%).
The main reason to investigate a thyroid nodule is to determine whether or not it is a thyroid cancer.
Blood tests (thyroid hormone levels), ultrasound and biopsy are the key components of investigating a thyroid nodule.
What types of cancers occur in the thyroid gland?
There are four main types of thyroid cancer:
- Papillary thyroid cancer - the most common
- Follicular thyroid cancer - also common
- Medullary thyroid cancer - rare
- Anaplastic thyroid cancer - very rare
Reassuringly, for most patients, papillary thyroid cancer has an excellent prognosis (survival >95%). Surgery is the main component of treatment for thyroid cancer (see here for a discussion of thyroidectomy)